A. Affirmative
Agreement
When indicating that
one person or thing does something and then adding that another does the same,
use the word “so” or “too”. To avoid needless repetition of words from the
affirmative statement, use the conjunction “and”, followed by a simple statement
using so or too. The order of this statement will depend on whether so or too
is used.
• When a form of the verb be is used in the main clause, the same tense of verb
be is used in the simple statement that follows.
Affirmative statement (be) + and + [ S + verb (be) + too]
Example: I am happy and you are too.
Affirmative statement (be) + and + [ so + verb (be) + S ]
Example: I am happy and so are you.
• When a compound verb (auxiliary +verb), for example, will go, should do, has
done, have written, must examine, etc., occurs in the main clause, the
auxiliary of the main verb is used in the simple statement, and the subject and
verb must agree.
Affirmative statement (compound verb) + and + [ S + auxiliary only + too ]
Example: Edward should do his homework and Bella should too.
Affirmative statement (compound verb) + and + [ so + auxiliary only + S ]
Example: Edward should do his homework and so does Bella.
• When any verb except be appears without any auxiliaries in the main clause,
the auxiliary do, does, or did is used in the simple statement. The subject and
verb must agree and the tense must be the same.
Affirmative statement (single verb except be) + and + [ S + do, does ,or did +
too ]
Example: Tae Yeon plays guitar every day and Jessica does too.
Affirmative statement (single verb except be) + and + [ so + do, does, or did +
S ]
Example: Yuri sung “Gee” and so did Yoona.
Additional Examples:
1. She has already written her composition, and so have her friends.
2. Their plane is arriving at nine o’clock, and so is mine.
3. I should go grocery shopping this afternoon, and so should my neighbor.
4. We like to swim in the pool, and they do too.
5. Our Spanish teacher loves to travel, and so do we.
B. Negative Agreement
“Either” and
“neither” function in simple statements much like “so” and “too” in affirmative
sentences. However, either and neither are used to indicate negative agreement.
The same rules for auxiliaries, be and do, does, or did apply.
Negative statement + and + [ S + negative auxiliary or be + either]
Negative statement + and + [ neither + positive auxiliary or be + S ]
Examples:
I didn’t see Bella this morning. Edward didn’t see Bella this morning
I didn’t see Bella this morning and Edward didn’t either.
I didn’t see Bella this morning and neither did Edward.
Additional examples:
1. The children shouldn’t take that medicine, and neither should she.
2. We don’t plan to attend the concert, and neither do they.
3. I don’t like tennis, and he doesn’t either.
4. She didn’t see anyone she knew, and neither did Tim.
5. The Yankees couldn’t play due to the bad weather, and neither could the
Angels.
A.
Verbs as Complements
1) This construction is used
with the verbs listed below:
Examples:
I enjoy studying English at
the CBA.
He considered traveling to
Europe for the summer, but he doesn’t have enough funds.
2) This construction is used with the verbs listed below:
Examples:
I decided to refuse the
invitation.
He pretended to be someone
else.
She forgot to bring her
keys.
3) With the
following Verbs the Sentence doesn’t change meaning if you use the
gerund (ing) or the infinitive
4) With the
following Verbs the Sentence has Different Meaning
Example:
She stopped studying Engineering when she got
pregnant.
Meaning she won’t study
Engineering any more. She stopped studying forever.
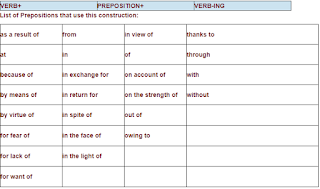
5) Use of
prepositions with the -Ing Form
EXCEPTION: But, except.
Example:
He hid the wallet, for fear of being stolen.
She was really famous, as a result of acting as Mary in
the Jesus Christ film.
Courage in
the Face of Eviction Nightmare
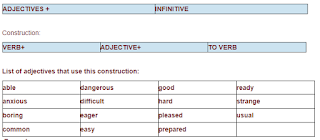
6) Use
of Adjectives with the infinitive form
Construction:
Examples:
I’m pleased to meet you
It’s difficult to
understand some people.
Rafael is eager to meet
you.
7) Use a Pronoun before the
Infinitive form
Certain verbs
require the following construction:
The pronouns to
be used are object pronouns: ME, YOU, HIM, HER, IT, US, YOU, THEM.
Example:
He orders her to study for
the test.
My mother promised me to
take me to the mall.
Rahima convinced him to
purchase an expensive purse.
8) Use the -ing (gerung)
form of a verb after the possessive form.
Example:
I understand her feeling.
9) Use of the verb need
with different nouns (living and things)
With living things use need
and the infinitive form of the verb.
The blender needs to be repaired.
The blanket needs to be
cleaned.












Komentar
Posting Komentar